Every device we rely on, from your home appliances to our traffic control system to the device you're reading this on now, relies on the magic of electrical circuits. Electrical circuits are the foundation for all electronics and understanding their basics is not only essential to anyone learning electronics, but useful to anyone who participates in the modern world. How circuits work can seem like a mystery full of technical terms and complex concepts, but the basics can be broken down in very simple terms. So explore with us: from what circuits are and what they do to how to best learn about circuits.
What is a electrical circuit?
An electrical circuit is a loop around which electricity moves to give power to the devices that make up the world around us. Imagine your friend has been helping you move, but after lifting so many heavy things, he’s out of energy. There are snacks in the kitchen to refuel, but the way there is blocked by stacks on stacks of boxes. Only by clearing a path to the kitchen and back can you bring him the energy he needs to keep performing the task. Circuits are the same thing: paths that can bring energy to the devices we want to perform various tasks.
If we have a power source with a negative and positive end, connecting the two lets us make a direct path from that negative start point to the positive endpoint - allowing the electricity to flow. If circuits sound like a “circle”, that’s because that’s not far off of what they are: simple circuits circle the electricity around themselves, from one end of the power source back to the other.
How do electrical circuits work?
If there is a path, tiny negatively charged particles called electrons like to move from negatively charged places—places with a lot of electrons—to positively charged places without many electrons. The energy those electrons bring is called electricity. Like stacks of boxes blocking your way to the kitchen, air usually does not allow electricity through easily, so we need the two sides to be connected with a material that does let electricity through easily, which is called a conductor. Metal wires work great for that and form many circuits.
What do circuits do?
The fact that electrical circuits move energy around lets us bring that energy in (and out) of all the tools we need for a modern world. If you want to have a device do something, like toast your bread or load your emails, you’ll need circuits to give it the power to do so.
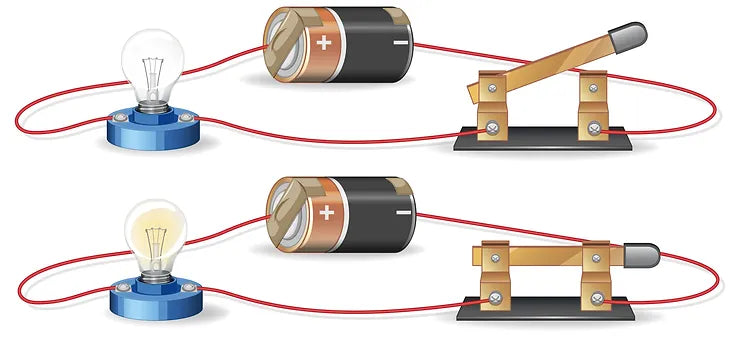
If a circuit is complete, meaning there is an unbroken path from start to finish, electricity will flow through each part of the circuit, including any connected devices. Those devices then have the power to do what they were meant to, and so your bedside lamp turns on or your electric vehicle starts to move. It can take a lot of imagination — and centuries of human innovation — to figure out all the practical applications we can get out of circuits, but discovering those endless possibilities is the most fun part!
What makes up a circuit?
What makes up an electrical circuit:
Electrical circuits are usually comprised of three key components:
-
A "path” made of conductive material that the electric current easily travels along, such as wire or etches in a circuit board.
-
A "source" of electrical power that gives the circuit electrical energy, such as batteries or a wall outlet
-
A "load”, made up of the device or devices that use that electrical power to operate such as lamps or motors
attribution: Image by brgfx on Freepik
What do circuit symbols mean?
An essential tool in the journey to understanding circuits will be the ability to read the circuit language. We’ll start you off with the most basic - ones you’ll see in almost any circuit.
The first represents a power source, like a battery. With a larger line representing the positive end (or terminal) and a smaller line representing the negative terminal, the power source is usually the start and endpoint of the electrical circuit.
The second represents a resistor, something on the circuit where electricity will still flow through, but it struggles more than it would in conductors like wires.
Why would we want to use a resistor if it restricts the flow of electricity and even uses up electrical energy? One of the main reasons is that a lot of materials do cool things when they resist electricity, like producing light or heat. From toasters to light bulbs, devices that heat or light up often “use” electricity by resisting it.
The last we’re going to talk about for now is a switch, represented by a place in the circuit where the lines don’t connect. When the switch is “off”, the circuit is open, which means there isn’t a path for the electricity to get to where it wants to go. No power is moving through and none of the devices on the way will work. Flip the switch and the circuit closes, giving the electricity a complete path to get to where it needs to go and powering the devices again.
There’s a lot more to learn about electrical circuits and the ways we understand or draw them, from voltage to alternating current versus direct current to so much more - but we believe in letting you learn with your hands as much as with your eyes, so let’s get your hands on them.
attribution: Image by brgfx on Freepik
How to learn about electronics or electrical circuits:
Explanations are nice, but the best and most engaging way to really understand circuits is to play around them.

EIM Technology provides numerous kits and accompanying guides to walk you through not just how to assemble basic circuits, but the principles at play in each one. With step by step instructions, these projects work great for all skill levels, from beginner to advanced, and most excitingly, will show you that you’re learning when the lights turn on or the motors start to move. What electrical circuits can do is a lot of fun, so make learning about them fun too!
We have carefully designed an experimental learning kit, including manual and tools, to coach you from introductory to intermediate level familiarity with electrical circuits:

Learn Basic Electrical Circuits in a Simple & Effective Way Using Our "Basic Electric Circuits" Learning Kit

"Basic Electric Circuits" Learning Kit by EIM Technology
Continue that journey with our other posts on different types of circuits, transistors, and resistance
Or make that journey an engaging, self guided exploration with kits that suit any level.
Happy learning!
Check our collections:
https://www.eimtechnology.com/





































